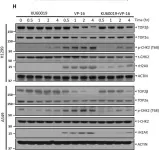
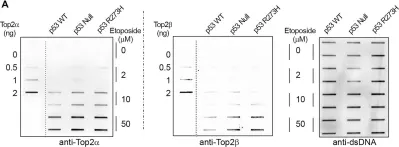
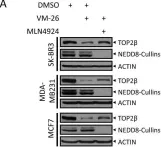
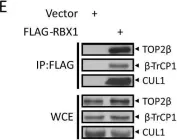
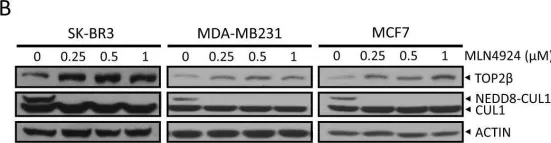
Topoisomerase II alpha and beta (TOP2A and TOP2B) isoenzymes perform essential and non-redundant cellular functions. Anthracyclines induce their potent anti-cancer effects primarily via TOP2A, but at the same time they induce a dose limiting cardiotoxicity through TOP2B. Here we describe the development of the obex class of TOP2 inhibitors that bind to a previously unidentified druggable pocket in the TOP2 ATPase domain to act as allosteric catalytic inhibitors by locking the ATPase domain conformation with the capability of isoform-selective inhibition. Through rational drug design we have developed topobexin, which interacts with residues that differ between TOP2A and TOP2B to provide inhibition that is both selective for TOP2B and superior to dexrazoxane. Topobexin is a potent protectant against chronic anthracycline cardiotoxicity in an animal model. This demonstration of TOP2 isoform-specific inhibition underscores the broader potential to improve drug specificity and minimize adverse effects in various medical treatments.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 18
In Nature Communications on 28 May 2025 by Kubeš, J., Karabanovich, G., et al.
In Cell Death & Disease on 23 January 2024 by Shu, J., Jiang, J., et al.
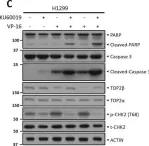
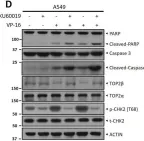
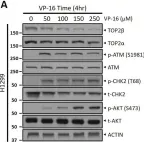
DNA topoisomerase II (TOP2) is an enzyme that performs a critical function in manipulating DNA topology during replication, transcription, and chromosomal compaction by forming a vital intermediate known as the TOP2-DNA cleavage complex (TOP2cc). Although the TOP2cc is often transient, stabilization can be achieved by TOP2 poisons, a family of anti-cancer chemotherapeutic agents targeting TOP2, such as etoposide (VP-16), and then induce double-strand breaks (DSBs) in cellular DNA. TOP2cc first needs to be proteolyzed before it can be processed by TDP2 for the removal of these protein adducts and to produce clean DNA ends necessary for proper repair. However, the mechanism by which TOP2βcc is proteolyzed has not been thoroughly studied. In this study, we report that after exposure to VP-16, MDM2, a RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase, attaches to TOP2β and initiates polyubiquitination and proteasomal degradation. Mechanistically, during exposure to VP-16, TOP2β binds to DNA to form TOP2βcc, which promotes MDM2 binding and subsequent TOP2β ubiquitination and degradation, and results in a decrease in TOP2βcc levels. Biologically, MDM2 inactivation abrogates TOP2β degradation, stabilizes TOP2βcc, and subsequently increases the number of TOP2β-concealed DSBs, resulting in the rapid death of cancer cells via the apoptotic process. Furthermore, we demonstrate the combination activity of VP-16 and RG7112, an MDM2 inhibitor, in the xenograft tumor model and in situ lung cancer mouse model. Taken together, the results of our research reveal an underlying mechanism by which MDM2 promotes cancer cell survival in the presence of TOP2 poisons by activating proteolysis of TOP2βcc in a p53-independent manner, and provides a rationale for the combination of MDM2 inhibitors with TOP2 poisons for cancer therapy.
© 2024. The Author(s).
-
Cell Biology
RAD54L2 counters TOP2-DNA adducts to promote genome stability.
In Science Advances on 8 December 2023 by D'Alessandro, G., Morales-Juarez, D. A., et al.
The catalytic cycle of topoisomerase 2 (TOP2) enzymes proceeds via a transient DNA double-strand break (DSB) intermediate termed the TOP2 cleavage complex (TOP2cc), in which the TOP2 protein is covalently bound to DNA. Anticancer agents such as etoposide operate by stabilizing TOP2ccs, ultimately generating genotoxic TOP2-DNA protein cross-links that require processing and repair. Here, we identify RAD54 like 2 (RAD54L2) as a factor promoting TOP2cc resolution. We demonstrate that RAD54L2 acts through a novel mechanism together with zinc finger protein associated with tyrosyl-DNA phosphodiesterase 2 (TDP2) and TOP2 (ZATT/ZNF451) and independent of TDP2. Our work suggests a model wherein RAD54L2 recognizes sumoylated TOP2 and, using its ATPase activity, promotes TOP2cc resolution and prevents DSB exposure. These findings suggest RAD54L2-mediated TOP2cc resolution as a potential mechanism for cancer therapy resistance and highlight RAD54L2 as an attractive candidate for drug discovery.
-
WB
-
Genetics
Topoisomerase II Inhibition Attenuates LPS-induced IL- 1β Secretion by Macrophages
Preprint on Research Square on 30 May 2023 by Brindle, A., Bainbridge, C., et al.
Inhibiting pathological secretion of Interleukin-1β has shown beneficial effects in disease models and in the clinic and thus there is interest in finding inhibitors that can reduce its release from macrophages in response to their activation by foreign pathogens. We used an in vitro human macrophage model to investigate whether ICRF-193, a Topoisomerase II inhibitor could modulate IL1B mRNA expression and IL-1β secretion. These macrophage-like cells readily secrete IL-1β in response to Lipopolysaccharide (LPS). Upon exposure to a non-toxic dose of ICRF-193, IL-1β secretion was diminished by ~ 40%; however, level of transcription of IL1B was unaffected. We show that there was no Topoisomerase 2B (TOP2B) binding to IL1B gene proximal sites, confirming that it is not involved directly in mediating the transcription of IL1B and hence why ICRF-193 does not alter IL1B mRNA levels. Quantification of Topoisomerase isoforms suggests that TOP2B plays a role in mediating the effects of ICRF-193 on IL-1β secretion. Hence, we show for the first time that ICRF-193 can reduce IL-1β secretion. Its low cost and the development of water-soluble prodrugs of ICRF-193 warrants its further investigation in the modulation of pathological secretion of this cytokine for the treatment of inflammatory disorders. (196 words)
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Replication-associated formation and repair of human topoisomerase IIIα cleavage complexes.
In Nature Communications on 6 April 2023 by Saha, L. K., Saha, S., et al.
Topoisomerase IIIα (TOP3A) belongs to the conserved Type IA family of DNA topoisomerases. Here we report that human TOP3A is associated with DNA replication forks and that a "self-trapping" TOP3A mutant (TOP3A-R364W) generates cellular TOP3A DNA cleavage complexes (TOP3Accs). We show that trapped TOP3Accs that interfere with replication, induce DNA damage and genome instability. To elucidate how TOP3Accs are repaired, we explored the role of Spartan (SPRTN), the metalloprotease associated with DNA replication, which digests proteins forming DNA-protein crosslinks (DPCs). We find that SPRTN-deficient cells show elevated TOP3Accs, whereas overexpression of SPRTN lowers cellular TOP3Accs. SPRTN is deubiquitinated and epistatic with TDP2 in response to TOP3Accs. In addition, we found that MRE11 can excise TOP3Accs, and that cell cycle determines the preference for the SPRTN-TDP2 vs. the ATM-MRE11 pathways, in S vs. G2, respectively. Our study highlights the prevalence of TOP3Accs repair mechanisms to ensure normal DNA replication.
© 2023. This is a U.S. Government work and not under copyright protection in the US; foreign copyright protection may apply.
-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
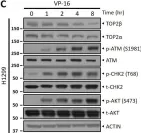
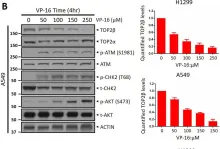
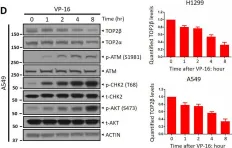
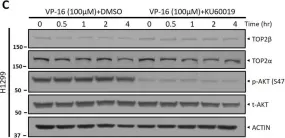
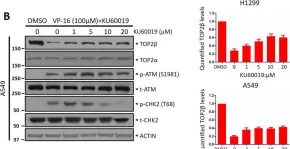
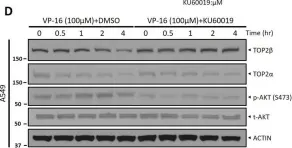
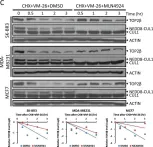
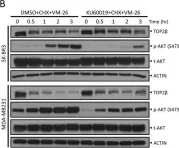
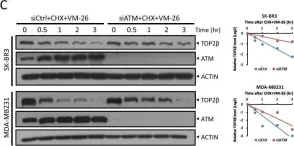
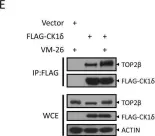
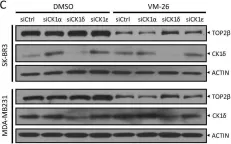
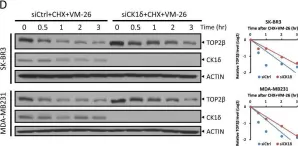
In Sci Rep on 17 January 2023 by Shu, J., Wang, X., et al.
Fig.1.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
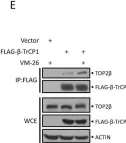
In Sci Rep on 17 January 2023 by Shu, J., Wang, X., et al.
Fig.1.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
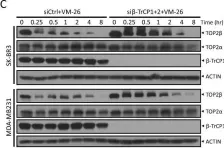
In Sci Rep on 17 January 2023 by Shu, J., Wang, X., et al.
Fig.1.D

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
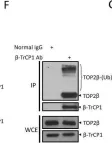
In Sci Rep on 17 January 2023 by Shu, J., Wang, X., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
In Sci Rep on 17 January 2023 by Shu, J., Wang, X., et al.
Fig.2.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
In Sci Rep on 17 January 2023 by Shu, J., Wang, X., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
In Sci Rep on 17 January 2023 by Shu, J., Wang, X., et al.
Fig.2.D

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
In Sci Rep on 17 January 2023 by Shu, J., Wang, X., et al.
Fig.2.F

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
In Sci Rep on 17 January 2023 by Shu, J., Wang, X., et al.
Fig.4.H

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
In Sci Rep on 17 January 2023 by Shu, J., Wang, X., et al.
Fig.6.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
In Sci Rep on 17 January 2023 by Shu, J., Wang, X., et al.
Fig.6.D

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
In Sci Rep on 17 January 2023 by Shu, J., Wang, X., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
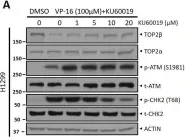
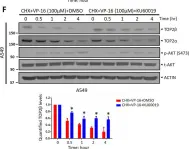
In Oncotarget on 19 February 2022 by Menendez, D., Anand, J. R., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Oncotarget by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
In Oncogenesis on 3 February 2020 by Shu, J., Cui, D., et al.
Fig.1.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncogenesis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
In Oncogenesis on 3 February 2020 by Shu, J., Cui, D., et al.
Fig.1.E

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncogenesis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
In Oncogenesis on 3 February 2020 by Shu, J., Cui, D., et al.
Fig.1.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncogenesis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
In Oncogenesis on 3 February 2020 by Shu, J., Cui, D., et al.
Fig.1.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncogenesis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
In Oncogenesis on 3 February 2020 by Shu, J., Cui, D., et al.
Fig.2.E

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncogenesis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
In Oncogenesis on 3 February 2020 by Shu, J., Cui, D., et al.
Fig.2.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncogenesis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
In Oncogenesis on 3 February 2020 by Shu, J., Cui, D., et al.
Fig.2.F

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncogenesis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
In Oncogenesis on 3 February 2020 by Shu, J., Cui, D., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncogenesis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
In Oncogenesis on 3 February 2020 by Shu, J., Cui, D., et al.
Fig.4.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncogenesis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
In Oncogenesis on 3 February 2020 by Shu, J., Cui, D., et al.
Fig.5.E

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncogenesis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
In Oncogenesis on 3 February 2020 by Shu, J., Cui, D., et al.
Fig.5.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncogenesis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30
In Oncogenesis on 3 February 2020 by Shu, J., Cui, D., et al.
Fig.5.D

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Oncogenesis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 30