An extracellular matrix (ECM) gene expression pattern (ECM3) distinguished truly aggressive grade III breast carcinomas (BCs). Here, we examined the biomechanical characteristics of the ECM in human BCs to identify the molecules that mediate the aggressiveness of ECM3/grade III (E3G3) tumors. By shotgun proteomics of decellularized human BCs, we found a significant enrichment in proteins involved in tumor-ECM interaction in E3G3 tumors. These tumors were characterized by high dense collagen deposition, a fibrillary cytoskeleton network and the highest stiffness. CLEC3A, a secreted C-type lectin domain family 3 member, was found unique of E3G3 tumors and was validated to be more expressed in these tumors by immunohistochemistry in 2 human BC cohorts, associating significantly with worse prognosis. Ectopic CLEC3A overexpression in MDA-MB-231, MDA-MB-361, and MDA-MB-468 BC cells increased intracellular mediators of tumor adhesion to the ECM, actin-stress fibers and YAP activation, and tumor migration. Accordingly, levels of the YAP/TAZ gene signature were higher in CLEC3A-positive ECM3-enriched tumors and correlated with tumor stiffness. These results implicate CLEC3A in mediating the ability of E3G3 BCs to sense cues in the surrounding ECM, accelerating tumor progression.
© 2025. The Author(s).
Product Citations: 38
In NPJ Breast Cancer on 6 June 2025 by Triulzi, T., Giussani, M., et al.
-
WB
-
Cancer Research
Role of the androgen receptor in melanoma aggressiveness.
In Cell Death & Disease on 21 January 2025 by Di Donato, M., Cristiani, C. M., et al.
Malignant melanoma represents the fifth most common cancer in the world and its incidence is rising. Novel therapies targeting receptor tyrosine kinases, kinases and immune checkpoints have been employed with a significant improvement of the overall survival and long-term disease containment. Nevertheless, the disease often progresses and becomes resistant to the therapies. As such, the discovery of new targets and drugs for advanced melanoma still remains a difficult task. Gender disparities, with a female advantage in melanoma incidence and outcome, have been reported. Although emerging studies support the pro-tumorigenic role of androgen/androgen receptor axis in melanoma, the molecular bases of such evidence are still under intense investigation. We now report that ligand activation of the androgen receptor drives melanoma invasiveness and its escape from natural killer-mediated cytotoxic effect. By combining different experimental approaches, we observe that melanoma escape is mediated by the androgen-triggered shedding of the surface molecule MICA. Specific blockade of ADAM10 or androgen receptor impairs the androgen-induced MICA shedding and melanoma immune-escape. Further, the increase in MICA serum levels correlates with a poor outcome in melanoma patients treated with the anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibody, pembrolizumab. At last, melanoma cells depleted of the androgen receptor become more responsive to the most commonly used immunocheckpoint inhibitors, suggesting that the receptor dampens the immunotherapy efficacy. Taken together, our findings identify the androgen receptor as a diagnostic guidance in melanoma and support the repositioning of AR blockers in clinical management of patients.
© 2025. The Author(s).
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
In International Journal of Molecular Sciences on 18 October 2024 by Gráczer, E., Pászty, K., et al.
Mechanotransduction, the process of how cells sense and convert mechanical stimuli into biochemical response, is crucial in the migration of leukocytes or cancer cells through the endothelium during inflammation or metastasis. Migrating cells exert forces on the endothelium through cell surface adhesion molecules, such as platelet endothelial adhesion molecule PECAM-1, and this is essential for a successful transmigration. To study PECAM-1-mediated mechanotransduction, we applied PECAM-1-antibody-coated magnetic beads and exerted about 40 pN force on the endothelial monolayer. We show that force increases cell-ECM adhesion in the cell center and is accompanied by the opening of cell-cell junctions. Upon depletion of the MEK/ERK kinase, BRAF force increases cell-ECM adhesion both at the cell periphery and in the cell center, but this does not result in the opening of cell-cell junctions. Decreasing cell-ECM adhesion in BRAF-depleted cells through FAK inhibition results in the remodeling of cell-cell junctions. Force-induced increase in cell-ECM adhesion in the cell center correlates with the activation of the transcriptional cofactor Yes-associated protein (YAP). Furthermore, the induced activation of YAP through LATS inhibition prevents junctional remodeling in control cells. Thus, the activation of YAP might determine the strength of cell-cell junctions during PECAM-1-mediated mechanotransduction.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
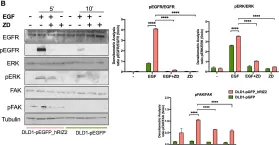
RIZ2 at the crossroad of the EGF/EGFR signaling in colorectal cancer.
In Journal of Translational Medicine on 18 October 2023 by Di Donato, M., Di Zazzo, E., et al.
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is the third most deadly and fourth most diagnosed cancer worldwide. Despite the progress in early diagnosis and advanced therapeutic options, CRC shows a poor prognosis with a 5 year survival rate of ~ 45%. PRDM2/RIZ, a member of PR/SET domain family (PRDM), expresses two main molecular variants, the PR-plus isoform (RIZ1) and the PR-minus (RIZ2). The imbalance in their expression levels in favor of RIZ2 is observed in many cancer types. The full length RIZ1 has been extensively investigated in several cancers where it acts as a tumor suppressor, whereas few studies have explored the RIZ2 oncogenic properties. PRDM2 is often target of frameshift mutations and aberrant DNA methylation in CRC. However, little is known about its role in CRC.
We combined in-silico investigation of The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) CRC datasets, cellular and molecular assays, transcriptome sequencing and functional annotation analysis to assess the role of RIZ2 in human CRC.
Our in-silico analysis on TCGA datasets confirmed that PRDM2 gene is frequently mutated and transcriptionally deregulated in CRC and revealed that a RIZ2 increase is highly correlated with a significant RIZ1 downregulation. Then, we assayed several CRC cell lines by qRT-PCR analysis for the main PRDM2 transcripts and selected DLD1 cell line, which showed the lowest RIZ2 levels. Therefore, we overexpressed RIZ2 in these cells to mimic TCGA datasets analysis results and consequently to assess the PRDM2/RIZ2 role in CRC. Data from RNA-seq disclosed that RIZ2 overexpression induced profound changes in CRC cell transcriptome via EGF pathway deregulation, suggesting that RIZ2 is involved in the EGF autocrine regulation of DLD1 cell behavior. Noteworthy, the forced RIZ2 expression increased cell viability, growth, colony formation, migration and organoid formation. These effects could be mediated by the release of high EGF levels by RIZ2 overexpressing DLD1 cells.
Our findings add novel insights on the putative RIZ2 tumor-promoting functions in CRC, although additional efforts are warranted to define the underlying molecular mechanism.
© 2023. BioMed Central Ltd., part of Springer Nature.
-
WB
-
Cancer Research
In Nature Communications on 25 April 2023 by Gao, G., Li, X., et al.
The outgrowth of epithelial bud followed by reiterated bifurcations during renal development is driven by the ligand-receptor interactions between the epithelium and the surrounding mesenchyme. Here, by exploring ligand-receptor interactions in E10.5 and E11.5 kidneys by single cell RNA-seq, we find that Isthmin1 (Ism1), a secreted protein, resembles Gdnf expression and modulates kidney branching morphogenesis. Mice deficient for Ism1 exhibit defective ureteric bud bifurcation and impaired metanephric mesenchyme condensation in E11.5 embryos, attributable to the compromised Gdnf/Ret signaling, ultimately leading to renal agenesis and hypoplasia/dysplasia. By HRP-induced proximity labelling, we further identify integrin α8β1 as a receptor of Ism1 in E11.5 kidney and demonstrate that Ism1 promoted cell-cell adhesion through interacting with Integrin α8β1, the receptor whose activation is responsible for Gdnf expression and mesenchyme condensation. Taken together, our work reveals Ism1 as a critical regulator of cell-cell interaction that modulates Gdnf/Ret signaling during early kidney development.
© 2023. The Author(s).
In J Transl Med on 18 October 2023 by Di Donato, M., Di Zazzo, E., et al.
Fig.7.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from J Transl Med by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
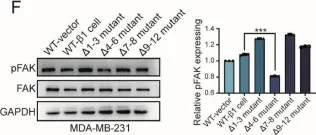
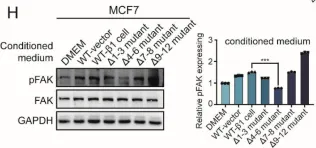
In Int J Mol Sci on 10 February 2021 by Cao, L., Wu, Y., et al.
Fig.2.F

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
In Int J Mol Sci on 10 February 2021 by Cao, L., Wu, Y., et al.
Fig.3.H

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Int J Mol Sci by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4
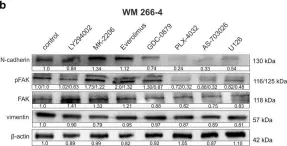
In Hum Cell on 1 January 2020 by Ciołczyk-Wierzbicka, D., Gil, D., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Hum Cell by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 4