Anticancer strategies using natural products or derivatives are promising alternatives for cancer treatment. Here, we showed that licochalcone D (LCD), a natural flavonoid extracted from Glycyrrhiza uralensis Fisch, suppressed the growth of breast cancer cells, and was less toxic to MCF-10A normal breast cells. LCD-induced DNA damage, cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis in breast cancer cells. Furthermore, LCD potentiated tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-induced cytotoxicity. Mechanistically, LCD was revealed to reduce survival protein expression and to upregulate death receptor 5 (DR5) expressions. Silencing DR5 blocked the ability of LCD to sensitize cells to TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. LCD increased CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein homologous protein (CHOP) expression in breast cancer cells. Knockdown of CHOP attenuated DR5 upregulation and apoptosis triggered by cotreatment with LCD and TRAIL. Furthermore, LCD suppressed the phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase and promoted the phosphorylation of c-Jun amino-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). Pretreatment with JNK inhibitor SP600125 or p38 MAPK inhibitor SB203580 abolished the upregulation of DR5 and CHOP, and also attenuated LCD plus TRAIL-induced cleavage of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. Overall, our results show that LCD exerts cytotoxic effects on breast cancer cells and arguments TRAIL-mediated apoptosis by inhibiting survival protein expression and upregulating DR5 in a JNK/p38 MAPK-CHOP-dependent manner.
© 2024 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Product Citations: 10
In Journal of Biochemical and Molecular Toxicology on 1 July 2024 by Zhang, Y., Wang, L., et al.
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
In Aging Cell on 1 December 2023 by Vue, Z., Garza-López, E., et al.
During aging, muscle gradually undergoes sarcopenia, the loss of function associated with loss of mass, strength, endurance, and oxidative capacity. However, the 3D structural alterations of mitochondria associated with aging in skeletal muscle and cardiac tissues are not well described. Although mitochondrial aging is associated with decreased mitochondrial capacity, the genes responsible for the morphological changes in mitochondria during aging are poorly characterized. We measured changes in mitochondrial morphology in aged murine gastrocnemius, soleus, and cardiac tissues using serial block-face scanning electron microscopy and 3D reconstructions. We also used reverse transcriptase-quantitative PCR, transmission electron microscopy quantification, Seahorse analysis, and metabolomics and lipidomics to measure changes in mitochondrial morphology and function after loss of mitochondria contact site and cristae organizing system (MICOS) complex genes, Chchd3, Chchd6, and Mitofilin. We identified significant changes in mitochondrial size in aged murine gastrocnemius, soleus, and cardiac tissues. We found that both age-related loss of the MICOS complex and knockouts of MICOS genes in mice altered mitochondrial morphology. Given the critical role of mitochondria in maintaining cellular metabolism, we characterized the metabolomes and lipidomes of young and aged mouse tissues, which showed profound alterations consistent with changes in membrane integrity, supporting our observations of age-related changes in muscle tissues. We found a relationship between changes in the MICOS complex and aging. Thus, it is important to understand the mechanisms that underlie the tissue-dependent 3D mitochondrial phenotypic changes that occur in aging and the evolutionary conservation of these mechanisms between Drosophila and mammals.
© 2023 The Authors. Aging Cell published by the Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cell Biology
In Oncogenesis on 13 May 2021 by Wu, Y. W., Chao, M. W., et al.
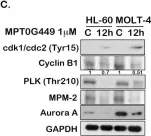
Acute leukemia is a highly heterogeneous disease; therefore, combination therapy is commonly used for patient treatment. Drug-drug interaction is a major concern of combined therapy; hence, dual/multi-target inhibitors have become a dominant approach for cancer drug development. HDACs and HSP90 are involved in the activation of various oncogenic signaling pathways, including PI3K/AKT/mTOR, JAK/STAT, and RAF/MEK/ERK, which are also highly enriched in acute leukemia gene expression profiles. Therefore, we suggest that dual HDAC and HSP90 inhibitors could represent a novel therapeutic approach for acute leukemia. MPT0G449 is a dual effect inhibitor, and it showed cytotoxic effectiveness in acute leukemia cells. Molecular docking analysis indicated that MPT0G449 possessed dual HDAC and HSP90 inhibitory abilities. Furthermore, MPT0G449 induced G2 arrest and caspase-mediated cell apoptosis in acute leukemia cells. The oncogenic signaling molecules AKT, mTOR, STAT3, STAT5, MEK, and ERK were significantly downregulated after MPT0G449 treatment in HL-60 and MOLT-4 cells. In vivo xenograft models confirmed the antitumor activity and showed the upregulation of acetyl-histone H3 and HSP70, biomarkers of pan-HDAC and HSP90 inhibition, with MPT0G449 treatment. These findings suggest that the dual inhibition of HDAC and HSP90 can suppress the expression of oncogenic pathways in acute leukemia, and MPT0G449 represents a novel therapeutic for anticancer treatment.
-
WB
-
Cancer Research
In Cancers on 1 April 2021 by Chen, X., Yang, D., et al.
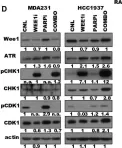
The identification of biomarker-driven targeted therapies for patients with triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) remains a major clinical challenge, due to a lack of specific targets. Here, we show that cyclin E, a major regulator of G1 to S transition, is deregulated in TNBC and is associated with mutations in DNA repair genes (e.g., BRCA1/2). Breast cancers with high levels of cyclin E not only have a higher prevalence of BRCA1/2 mutations, but also are associated with the worst outcomes. Using several in vitro and in vivo model systems, we show that TNBCs that harbor either mutations in BRCA1/2 or overexpression of cyclin E are very sensitive to the growth inhibitory effects of AZD-1775 (Wee 1 kinase inhibitor) when used in combination with MK-4837 (PARP inhibitor). Combination treatment of TNBC cell lines with these two agents results in synergistic cell killing due to induction of replicative stress, downregulation of DNA repair and cytokinesis failure that results in increased apoptosis. These findings highlight the potential clinical application of using cyclin E and BRCA mutations as biomarkers to select only those patients with the highest replicative stress properties that may benefit from combination treatment with Wee 1 kinase and PARP inhibitors.
-
WB
-
Cancer Research
-
Genetics
In Cell Death Discovery on 28 March 2018 by Marlier, Q., Jibassia, F., et al.
Cell cycle proteins are mainly expressed by dividing cells. However, it is well established that these molecules play additional non-canonical activities in several cell death contexts. Increasing evidence shows expression of cell cycle regulating proteins in post-mitotic cells, including mature neurons, following neuronal insult. Several cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) have already been shown to mediate ischemic neuronal death but Cdk1, a major cell cycle G2/M regulator, has not been investigated in this context. We therefore examined the role of Cdk1 in neuronal cell death following cerebral ischemia, using both in vitro and in vivo genetic and pharmacological approaches. Exposure of primary cortical neurons cultures to 4 h of oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) resulted in neuronal cell death and induced Cdk1 expression. Neurons from Cdk1-cKO mice showed partial resistance to OGD-induced neuronal cell death. Addition of R-roscovitine to the culture medium conferred neuroprotection against OGD-induced neuronal death. Transient 1-h occlusion of the cerebral artery (MCAO) also leads to Cdk1 expression and activation. Cdk1-cKO mice displayed partial resistance to transient 1-h MCAO. Moreover, systemic delivery of R-roscovitine was neuroprotective following transient 1-h MCAO. This study demonstrates that promising neuroprotective therapies can be considered through inhibition of the cell cycle machinery and particularly through pharmacological inhibition of Cdk1.
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Genetics
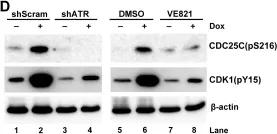
In Oncogenesis on 13 May 2021 by Wu, Y. W., Chao, M. W., et al.
Fig.3.C

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Oncogenesis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 7
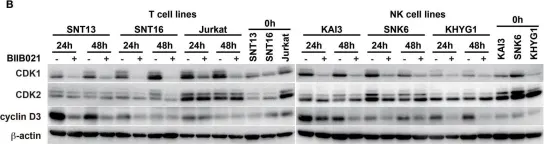
In Cancers (Basel) on 1 April 2021 by Chen, X., Yang, D., et al.
Fig.4.D

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Cancers (Basel) by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 7
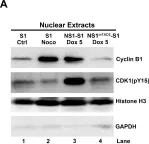
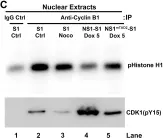
In PLoS Pathog on 1 March 2017 by Xu, P., Zhou, Z., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 7
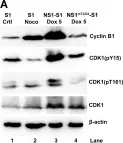
In PLoS Pathog on 1 March 2017 by Xu, P., Zhou, Z., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 7
In PLoS Pathog on 1 March 2017 by Xu, P., Zhou, Z., et al.
Fig.7.D

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 7
In PLoS Pathog on 1 March 2017 by Xu, P., Zhou, Z., et al.
Fig.4.C

-
WB
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS Pathog by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 7
In Front Microbiol on 29 April 2015 by Suzuki, M., Takeda, T., et al.
Fig.5.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Front Microbiol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 7