Demodex mites are commensal parasites of hair follicles (HFs). Normally asymptomatic, inflammatory outgrowth of mites can accompany malnutrition, immune dysfunction, and aging, but mechanisms restricting Demodex outgrowth are not defined. Here, we show that control of mite HF colonization in mice required group 2 innate lymphoid cells (ILC2s), interleukin-13 (IL-13), and its receptor, IL-4Ra-IL-13Ra1. HF-associated ILC2s elaborated IL-13 that attenuated HFs and epithelial proliferation at anagen onset; in their absence, Demodex colonization led to increased epithelial proliferation and replacement of gene programs for repair by aberrant inflammation, leading to the loss of barrier function and HF exhaustion. Humans with rhinophymatous acne rosacea, an inflammatory condition associated with Demodex, had increased HF inflammation with decreased type 2 cytokines, consistent with the inverse relationship seen in mice. Our studies uncover a key role for skin ILC2s and IL-13, which comprise an immune checkpoint that sustains cutaneous integrity and restricts pathologic infestation by colonizing HF mites.
Copyright © 2022 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Product Citations: 8
Innate type 2 immunity controls hair follicle commensalism by Demodex mites.
In Immunity on 11 October 2022 by Ricardo-Gonzalez, R. R., Kotas, M. E., et al.
-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Immunology and Microbiology
RET Regulates Human Medullary Thyroid Cancer Cell Proliferation through CDK5 and STAT3 Activation.
In Biomolecules on 9 June 2021 by Yue, C. H., Oner, M., et al.
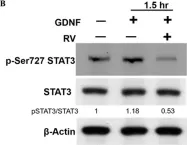
Medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) is a neuroendocrine tumor that arises from the parafollicular C-cells, which produces the hormone calcitonin. RET is a transmembrane receptor protein-tyrosine kinase, which is highly expressed in MTC. Our previous studies reported that cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (CDK5) plays a crucial role in cancer progression, including MTC. However, the role of CDK5 in GDNF-induced RET signaling in medullary thyroid cancer proliferation remains unknown. Here, we investigated RET activation and its biochemically interaction with CDK5 in GDNF-induced medullary thyroid cancer proliferation. Our results demonstrated that GDNF stimulated RET phosphorylation and thus subsequently resulted in CDK5 activation by its phosphorylation. Activated CDK5 further caused STAT3 activation by its specific phosphorylation at Ser727. Moreover, we also found that GDNF treatment enhanced ERK1/2 and EGR1 activity, which is involved in p35 activation. Interestingly, we identified for the first time that CDK5 physically interacted with RET protein in MTC. Overall, our results provide a new mechanism for medullary thyroid cancer cell proliferation, suggesting that targeting CDK5 may be a promising therapeutic candidate for human medullary thyroid cancer in the near future.
-
WB
-
Biochemistry and Molecular biology
-
Cancer Research
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
Rational Targeting of Cdc42 Overcomes Drug Resistance of Multiple Myeloma.
In Frontiers in Oncology on 22 October 2019 by Nguyen, P., Chakrabarti, J., et al.
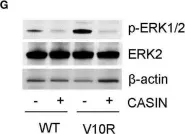
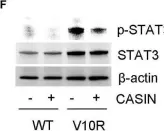
Multiple myeloma (MM) drug resistance highlights a need for alternative therapeutic strategies. In this study, we show that CASIN, a selective inhibitor of cell division cycle 42 (Cdc42) GTPase, inhibited proliferation and survival of melphalan/bortezomib-resistant MM cells more profoundly than that of the sensitive cells. Furthermore, CASIN was more potent than melphalan/bortezomib in inhibiting melphalan/bortezomib-resistant cells. In addition, CASIN sensitized melphalan/bortezomib-resistant cells to this drug combination. Mechanistically, Cdc42 activity was higher in melphalan/bortezomib-resistant cells than that in the sensitive cells. CASIN inhibited mono-ubiquitination of Fanconi anemia (FA) complementation group D2 (FANCD2) of the FA DNA damage repair pathway in melphalan-resistant but not melphalan-sensitive cells, thereby sensitizing melphalan-resistant cells to DNA damage. CASIN suppressed epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) activities to a larger extent in bortezomib-resistant than in melphalan-sensitive cells. Reconstitution of ERK activity partially protected CASIN-treated bortezomib-resistant cells from death, suggesting that CASIN-induced killing is attributable to suppression of ERK. Importantly, CASIN extended the lifespan of mouse xenografts of bortezomib-resistant cells and caused apoptosis of myeloma cells from bortezomib-resistant MM patients. Finally, CASIN had negligible side effects on peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from healthy human subjects and normal B cells. Our data provide a proof of concept demonstration that rational targeting of Cdc42 represents a promising approach to overcome MM drug resistance.
Copyright © 2019 Nguyen, Chakrabarti, Li, Kalim, Zhang, Zhang, Zheng and Guo.
-
WB
In Frontiers in Immunology on 9 March 2019 by Davies, R., Sarkar, I., et al.
Primary Sjögren's syndrome (pSS) is associated with polymorphisms and mRNA expression profiles that are indicative of an exaggerated innate and type I IFN immune response. Excessive activation potential of signaling pathways may play a role in this profile, but the intracellular signaling profile of the disease is not well characterized. To gain insights into potentially dysfunctional intracellular signaling profiles of pSS patients we conducted an exploratory analysis of MAPK/ERK and JAK/STAT signaling networks in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) from 25 female pSS patients and 25 female age-matched healthy donors using phospho-specific flow cytometry. We analyzed unstimulated samples, as well as samples during a 4 h time period following activation of Toll-like receptor (TLR) 7 and 9. Expression levels of MxA, IFI44, OAS1, GBP1, and GBP2 in PBMC were analyzed by real-time PCR. Cytokine levels in plasma were determined using a 25-plex Luminex-assay. Principal component analysis (PCA) showed that basal phosphorylation profiles could be used to differentiate pSS patients from healthy donor samples by stronger intracellular signaling pathway activation in NK and T cells relative to B cells. Stimulation of PBMC with TLR7 and -9 ligands showed significant differences in the phosphorylation profiles between samples from pSS patients and healthy donors. Including clinical parameters such as extraglandular manifestations (EGM), we observed stronger responses of NF-κB and STAT3 S727 in B cells from EGM-negative patients compared to EGM-positive patients and healthy controls. Plasma cytokine levels were correlated to the basal phosphorylation levels in these patients. In addition, 70% of the patients had a positive IFN score. These patients differed from the IFN score negative patients regarding their phosphorylation profiles and their plasma cytokine levels. In conclusion, we here report increased signaling potentials in peripheral B cells of pSS patients in response to TLR7 and -9 stimulation through STAT3 S727 and NF-κB that correlate with a type I IFN signature. Induction of these pathways could contribute to the generation of a type I IFN signature in pSS. Patients displaying elevated potentiation of STAT3 S727 and NF-κB signaling could therefore benefit from therapies targeting these pathways.
-
Immunology and Microbiology
In Oncotarget on 22 January 2019 by Laparra, J., Fotschki, B., et al.
Imbalances in innate immunity and the activity of innate immune cells are implicated in the development of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Plant seeds are good sources of protease inhibitors, which can have a significant influence on human health disorders, especially in the field of cancer prevention. To elucidate the impact and preventive effects of immunonutritional serine-type protease inhibitors (STPIs) on HCC, it was used an established model of chemically induced liver injury. Injured livers induced Akt as well as hepatic infiltration of NKG2D + and CD74 + cells. Feeding STPIs reduced size and number of intrahepatic nodes of mononuclear. These animals showed an inverse association of the severity of HCC with bioactive hepcidin levels, which was significantly correlated with the hepatic myeloperoxidase activity. According to their origin, administration of STPIs significantly induce increased numbers of F4/80 + cells in injured livers that can be responsible for the biological effects detected on the parenchyma and inflammatory markers under DEN/TAA treatment. These findings can have direct implications in HCC immunotherapy where enhanced response(s) in inflammation-driven cancer patients could help promoting inflammation-driven processes and favor tumor growth. Altogether, this study demonstrates that oral administration of STPIs modulate innate immunity response influencing HCC aggressiveness and progression. These results represent a path forward to develop durable, long-lasting response against hepatocarcinoma and open a future research path in the development of coadjutant intervention strategies to pharmacological therapies.
-
WB
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
-
Cancer Research
In Biomolecules on 9 June 2021 by Yue, C. H., Oner, M., et al.
Fig.3.B

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Biomolecules by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
In Front Oncol on 22 October 2019 by Nguyen, P., Chakrabarti, J., et al.
Fig.4.G

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Front Oncol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3
In Front Oncol on 22 October 2019 by Nguyen, P., Chakrabarti, J., et al.
Fig.4.F

-
WB
-
Collected and cropped from Front Oncol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 3