SPINT1, a membrane-anchored serine protease inhibitor, regulates cascades of pericellular proteolysis while its tissue-specific functions remain incompletely characterized. In this study, we generate Spint1-lacZ knock-in mice and observe Spint1 expression in embryonic pancreatic epithelium. Pancreas-specific Spint1 disruption significantly diminishes islet size and mass, causing glucose intolerance and downregulation of MAFA and insulin. Mechanistically, the serine protease HEPSIN interacts with SPINT1 in β cells, and Hepsin silencing counteracts the downregulation of Mafa and Ins1 caused by Spint1 depletion. Furthermore, we demonstrate a potential interaction between HEPSIN and GLP1R in β cells. Spint1 silencing or Hepsin overexpression reduces GLP1R-related cyclic AMP levels and Mafa expression. Spint1-disrupted mice also exhibit a significant reduction in Exendin-4-induced insulin secretion. Moreover, SPINT1 expression increases in islets of prediabetic humans compared to non-prediabetic groups. The results unveil a role for SPINT1 in β cells, modulating glucose homeostasis and insulin production via HEPSIN/MAFA signaling.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Applications
Reactivity
Research Area
In Nature Communications on 3 December 2024 by Lin, H. H., Yu, I. S., et al.
-
Endocrinology and Physiology
In Redox Biology on 1 November 2024 by Lin, Y. S., Tsai, Y. C., et al.
Cancer research is continuously exploring new avenues to improve treatments, and ferroptosis induction has emerged as a promising approach. However, the lack of comprehensive analysis of the ferroptosis sensitivity in different cancer types has limited its clinical application. Moreover, identifying the key regulator that influences the ferroptosis sensitivity during cancer progression remains a major challenge. In this study, we shed light on the role of ferroptosis in colorectal cancer and identified a novel ferroptosis repressor, NUDT16L1, that contributes to the ferroptosis insensitivity in this cancer type. Mechanistically, NUDT16L1 promotes ferroptosis insensitivity in colon cancer by enhancing the expression of key ferroptosis repressor and mitochondrial genes through direct binding to NAD-capped RNAs and the indirect action of MALAT1. Our findings also reveal that NUDT16L1 localizes to the mitochondria to maintain its proper function by preventing mitochondrial DNA leakage after treatment of ferroptosis inducer in colon cancer cells. Importantly, our orthotopic injection and Nudt16l1 transgenic mouse models of colon cancer demonstrated the critical role of NUDT16L1 in promoting tumor growth. Moreover, clinical specimens revealed that NUDT16L1 was overexpressed in colorectal cancer, indicating its potential as a therapeutic target. Finally, our study shows the therapeutic potential of a NUDT16L1 inhibitor in vitro, in vivo and ex vivo. Taken together, these findings provide new insights into the crucial role of NUDT16L1 in colorectal cancer and highlight its potential as a promising therapeutic target.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
-
Cancer Research
-
Cell Biology
In Biomedicines on 28 October 2022 by Cuenca, I., Martínez-Rojas, B., et al.
Fig.2.B

-
ICC
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
Collected and cropped from Biomedicines by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 18
In Biomedicines on 28 October 2022 by Cuenca, I., Martínez-Rojas, B., et al.
Fig.2.A

-
ICC
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
Collected and cropped from Biomedicines by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 18
In Fujita Med J on 4 February 2022 by Uga, N., Nakatani, M., et al.
Fig.5.B

-
IHC
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
Collected and cropped from Fujita Med J by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 18
In Fujita Med J on 4 February 2022 by Uga, N., Nakatani, M., et al.
Fig.5.A

-
IHC
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
Collected and cropped from Fujita Med J by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 18
In Fujita Med J on 4 February 2022 by Uga, N., Nakatani, M., et al.
Fig.6.B

-
IHC
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
Collected and cropped from Fujita Med J by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 18
In Fujita Med J on 4 February 2022 by Uga, N., Nakatani, M., et al.
Fig.6.A

-
IHC
-
Rattus norvegicus (Rat)
Collected and cropped from Fujita Med J by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 18
In Front Oncol on 20 May 2020 by Gong, L., Xiao, M., et al.
Fig.5.C,D

-
IHC
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from Front Oncol by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 18
In Cell Death Dis on 28 October 2019 by Burocziova, M., Burdová, K., et al.
Fig.4.E

-
IHC
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Dis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 18
In Cell Death Dis on 28 October 2019 by Burocziova, M., Burdová, K., et al.
Fig.3.F

-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Cell Death Dis by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 18
In BMC Cancer on 3 January 2019 by Lee, S. R., Kwon, S. W., et al.
Fig.4.B

-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from BMC Cancer by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 18
In Sci Rep on 7 August 2017 by Chen, H. C., Chin, Y. F., et al.
Fig.7.F

-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Sci Rep by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 18
In Nat Commun on 17 May 2016 by de Jong, P. R., Taniguchi, K., et al.
Fig.3.A

-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 18
In Nat Commun on 17 May 2016 by de Jong, P. R., Taniguchi, K., et al.
Fig.5.A

-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 18
In Nat Commun on 17 May 2016 by de Jong, P. R., Taniguchi, K., et al.
Fig.4.C

-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 18
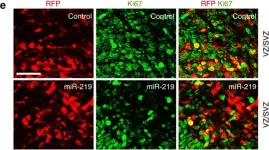
In Nat Commun on 11 March 2016 by Murai, K., Sun, G., et al.
Fig.4.A

-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 18
In Nat Commun on 11 March 2016 by Murai, K., Sun, G., et al.
Fig.6.D

-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 18
In Nat Commun on 11 March 2016 by Murai, K., Sun, G., et al.
Fig.3.E

-
IHC-IF
-
Mus musculus (House mouse)
Collected and cropped from Nat Commun by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 18
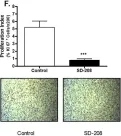
In PLoS One on 10 March 2015 by Tandon, M., Salamoun, J. M., et al.
Fig.6.F

-
IHC
-
Homo sapiens (Human)
Collected and cropped from PLoS One by CiteAb, provided under a CC-BY license
Image 1 of 18